Array
- Array is a collection of similar type of data.
- Array is of fixed size. Have to provide size of an array at creation time.
- Array can store primitive data type and non-primitive.
- Array itself is a non-primitive data type.
- To use array, you have to create object of array.
- Array is always based on index, index always start with 0 and manage by java.
- There are different types of array for example 1D, 2D, multi-dimensional array.
1-D Array
- Syntax to create 1-D array
- Declaration of Array
Data-Type NameOfArray[];
- Instance/Object creation of array
NameOfArray = new Data-Type[size];
- Initialization of array
NameOfArray[index] = value;
- Memory allocation of array
- 4-Ways to create array
1-ways
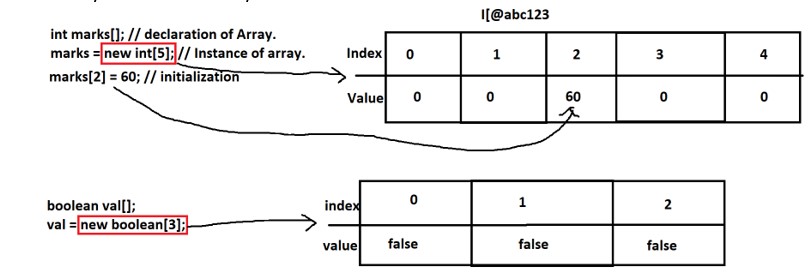
int marks[]; // declaration of Array.
marks = new int[5]; // Instance of array.
marks[0] = 78; // initialization of array.
marks[1] = 48;
marks[2] = 66;
marks[3] = 74;
marks[4] = 90;
2-ways
int marks[] = new int[5]; // declaration and Instance creation of array.
marks[0] = 78; // initialization of array.
marks[1] = 48;
marks[2] = 66;
marks[3] = 74;
marks[4] = 90;
3-ways
int marks[] = new int[]{78, 48, 66, 74, 90}; // declaration, instance & initialization
4-ways
int marks[] = {78, 48, 66, 74, 90}; // declaration, instance & initialization
- If you try to access an index which is not available then you will end up with following exception
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 12 out of bounds for length 12
2-D Array
- Is use to store data in form of row and column.
- Syntax
- Declaration of array
Data-type variablename[][];
- Instance/object creation of array
Variablename = new Data-type[row-size][column-size];
- Initialization of array
Variablename[row-index][column-index] = value;
- In 2-D array row size is always mandatory and column size is optional.
- Representation of 2-D arrays
- There are 4 ways to create 2-d array
1-Way
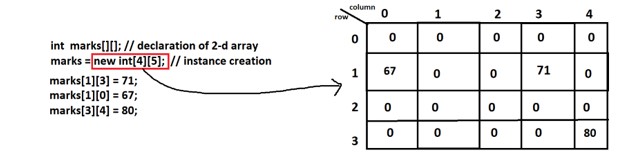
int marks[][]; // declaration
marks = new int[4][5]; // instance
marks[0][0] = 60; // initialization
marks[0][1] = 90;
marks[0][2] = 88;
marks[0][3] = 70;
marks[0][4] = 51;
2-Way
int marks[][] = new int[4][5]; // declaration and instance
marks[0][0] = 60; // initialization
marks[0][1] = 90;
marks[0][2] = 88;
marks[0][3] = 70;
marks[0][4] = 51;
3-Way
int marks[][] = new int[][] { {78,56,78,66,56}, {67,87,56,78,49}, {67,78,45,68,89}, {98,86,56,98,67} };
4-Way
int marks[][] = {{78,56,78,66,56}, {67,87,56,78,49}, {67,78,45,68,89}, {98,86,56,98,67}};
- Use Length in 2-D Array
System.out.println(marks.length); // it will return the total row count
System.out.println(marks[2].length); // it will return the total column count of specified row
Multi-dimensional/ Jagged Array
- In this type of array rows can have different number of columns.

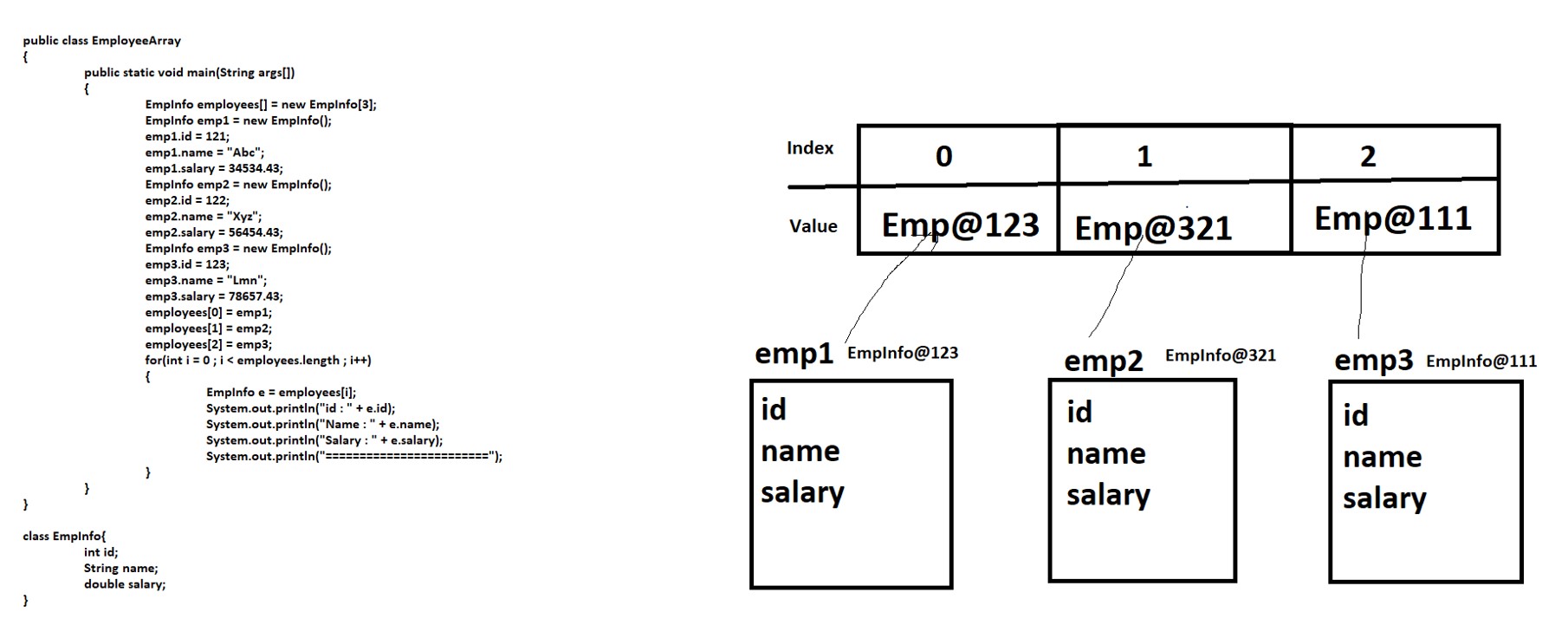
Using Array to store Custom Class Objects
Join Telegram : Click Here
All Full Stack Java Study Material
Job’s For Fresher
Share This Information To Your Friends and Your College Group’s, To Help Them !